|
This tab defines the queue and its
Data Input
Method,
Notification and
Archive properties.
Queue name must be supplied and
unique.
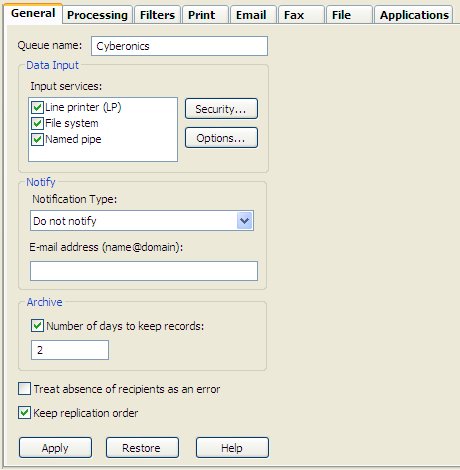
Three Input Services of Data
Input to FTSpooler are available:
Line
Printer(LP), File System, and Named Pipe.
Notify notifies users
about completion of a job via e-mail. Choose to
notify on success, notify on
error, or always notify, from
the Notification Type dropdown menu.
Enter a valid
email in the E-mail address line.
Archive enables you to specify the
Number of days to keep the records for
this queue.
No recipient to the queue is reported as an error if
the option Treat absence of recipients as an
error is checked. This reports an error when no
direct output (such as an email recipient) is activated
for a document.
Keep replication order processes split
documents from the one input file in arrival order,
effectively single-threading the queue. This is the
default and can be unticked. Unticking allows multiple
threads (to the limit in Setup, Settings,
Maximum ... threads) meaning the job will process
faster with unpredictable output order.
Click the Apply button to save the
changes.
|


