Queue Properties
Select the queue to change by highlighting it. Update the queue settings in the Properties Bar on the right side of the FormTrap Server Window.
General Tab
This tab defines the queue and its Data Input method, Notification and Archive properties.
Queue name must be supplied and unique.
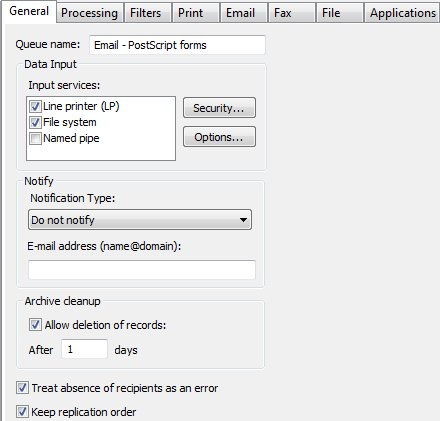
Three Data Input, Input Services are available: Line Printer (LP), File System, and Named Pipe.
- Line printer allows users to treat the queue
as a printer. You may:
- use lp/lpr from Unix, see More information on Unix LPR Printers
define and write to an LPR printer from Windows, see More information on Windows LPR Printers
use a "Work Station Customization Object" from a AS/400 to "print" files directly to the queue, email Support@FormTrap.com or see the PDF on AS/400 HERE.
- use lp/lpr from Unix, see More information on Unix LPR Printers
- File system allows the user's application or a copy statement to write a file directly to the queue folder. Queue folders are by default located under the %fthome%\data folder (%fthome% folder is shown in Setup, Core Components). This is the normal path and file name to the queue folder Sample Queue, file name can be constant:
- C:\fthome\v8\data\Sample Queue\filename.txt
- More information on File system
- Named pipe allows the user to pipe data from their application to a queue, provided the application is able to directly use a pipe. FormTrap Server generates a pipe called \\ServerName\pipe\QueueName (where ServerName is replaced with "." (dot) if writing from an application to the queue on the same machine).
- More information on Named pipe
- Note: If none of the above File input methods are selected, the queue cannot function and is automatically deleted on Save.
Notify notifies users about completion of a job via e-mail. Choose to notify on success, notify on error, or always notify, from the Notification Type dropdown menu. Enter a valid email in the E-mail address line.
Archive Cleanup enables you to tick if deletion of records is allowed, and if ticked, how many days to keep the records for this queue. Unticked means keep records for ever. Number of days is how many days records are kept (minimum 1 day). Expired entries are automatically purged several times per day.
Treat absence of recipients as an error ticked reports an error when no direct output (such as email) is activated for a document. Use this to report a document where you expect a direct recipient (normally Fax or Email address missing from the document).
Keep replication order processes split documents from the one input file in arrival order, effectively single-threading the queue. This is the default and can be unticked. Unticking allows multiple threads (to the limit in Setup, Settings, Maximum ... threads) meaning the job will process faster with unpredictable output order.
Click the Apply button to save the changes.
Security for File system and Named pipe
This setting determines which users or groups have write permission to this queue, meaning you have tight security control over who is allowed to send data to FormTrap Server. Default is the common selection and provides the same inherited security setting as the folder above the queue folder. Unrestricted provides full write permissions to all users while Access control list allows addition/removal of specific users or groups allowed to write to this queue.
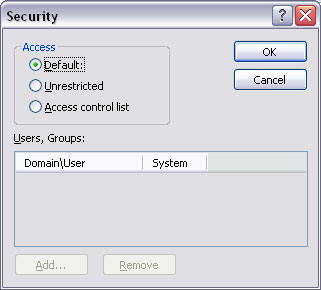
To add the Users or Groups for Access control option, click Add button and enter Name and System name for the user.
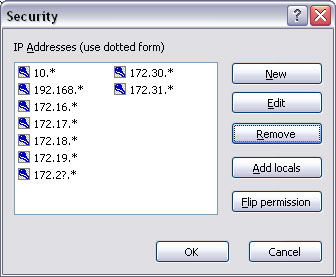
The Line printer selection (unlike File system and Named pipe) uses IP Addresses to secure jobs. The Add locals button automatically adds all local IP Addresses to the list. Flip permission allows the selected IP Address permissions to be set to the reverse of what is currently shown (i.e. locked or unlocked).
File system: Folder options
In this dialogue box define whether this queue folder is shared across the network:
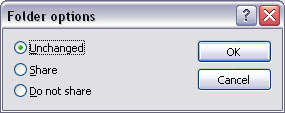
- Unchanged - FormTrap Server does share or remove share for the folder. The system administrator takes responsibility for sharing this folder on the network.
- Share makes the queue folder available as a network shared object.
- Do not share hides this folder from the network.
Named pipe options
This allows the pipe type to be defined as either Asynchronous (returns control immediately meaning the transfer takes place as a background task) or Synchronous (meaning the pipe maintains the current thread until data has been transferred). For synchronous pipes, enter the Number of instances (concurrent instances), keeping this number as low as possible.
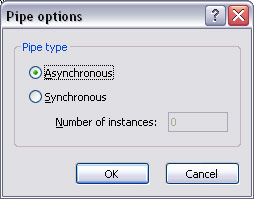
- Asynchronous: number of users is not limited.
- Synchronous: number of instances controls how many users can use the pipe simultaneously.



